Serum interleukin-6 is associated with hypocalcemia, hypoferritinemia and hyperkalemia in end-stage renal disease patients
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Authors
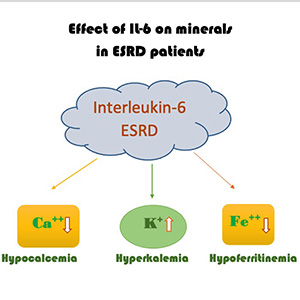
Both of chronic inflammation and mineral disturbance are major concerns in patients with chronic kidney disease, particularly end-stage renal disease (ESRD). The present study aimed to investigate the association between circulating interleukin-6 (IL-6) and minerals dysregulation in patients diagnosed with ESRD and on a continuous hemodialysis regimen. This cross-sectional study included 74 patients undergoing continuous hemodialysis. Serum samples were tested for IL-6 using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Mineral were analyzed using an electrolyte analyzer and biochemical tests. Parameter correlations were analyzed using the Pearson’s correlation test. Among the studies group, the male: female ratio was 1:0.72. IL-6 mean value was 13.77 pg/mL ±9.79 SD. IL-6 was significantly negatively correlated with circulating iron and calcium levels (r= –0.229, P=0.049; r= –0.252, P=0.03, respectively). IL-6 was significantly positively correlated with K+ levels (r=0.269, P=0.02). The present study highlighted the substantial role of IL-6 in mineral dysregulation in hemodialysis patients. However, identifying IL-6 as potential therapeutic target for minimizing and monitoring clinical effects of mineral disturbances in hemodialysis patients still requires further confirmatory studies.
How to Cite

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
PAGEPress has chosen to apply the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0) to all manuscripts to be published.








